There is no way to think about a Digital Marketing structure without social media and an organic search.
At the end of the day the niche or business model don’t matter, users always use a social network at some point of their buying process or search for a term on Google that you can include in some of your contents ranked by Google.
So, have you ever imagined how both activities are solved with just one action? This is exactly what we are going to focus on in this post: how can social media content help with SEO results.
How does Google understand social media?
We use Google because it’s the main search engine.
According to global data from StatCounter Global Stats, Google is the most used search engine around: collecting 89,94% in comparison with 4,37% for Bing and 3,93% for Yahoo.
In Latin America, this trend is the same. The numbers speak for themselves:
- Colombia: 95,21% for Google searches, 4,11% for Bing and 0,36% for Yahoo
- Brazil: 96% for Google, 3,28% for Bing and 0,57% for Yahoo
- Chile: 96,25% corresponds to Google, 3,31% to Bing and 0,18% to Yahoo.
Since this is the case, all the SEO efforts focus on Google.
To start with, it’s important to understand how Google interprets social media.
A search on Google is made up from several algorithms that interpret hundreds of positioning factors (meaning, classification variables that come into play when a page is displayed). Since they are assigned to a site, these algorithms place search results of a site in a certain location.
In the past, many said that social interactions were one of the factors that Google considered when it provided rankings. However, Google treats social media as a web page and not as a factor (it’s important to remember that social presence is a positioning factor).
Therefore, not all published content on a social network, even if it’s indexed, can be indexed.
As I mentioned earlier, Google is made up of various algorithms that interpret content quality, veracity, and influence, among other factors. Therefore, published content on social media can eventually get a good SERP (search results page position).
Google doesn’t always index a social media update, even if the update or entry isn’t a positioning factor.
If social media is not a classification factor, should I forget about this for SEO? NO!
Google uses Google+ signs, for example, to interpret some local results and uses data on Twitter to discover new content (Google has a partnership with Twitter).
How to use networks to improve SEO results
Have you ever stopped to think that social media can be a search mechanism? Networks such as Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter use hashtags that can provide keywords to work with.
In addition, Google has its own social media: Google +, used in some rich SERP results.
Here are a number of possible applications for social media so you can improve your SEO results.
1.- Do you have a local business? Use Google My Business
Google’s algorithms are responsible for local searches and have a geolocation set in place.
One of them is Pigeon, an algorithm that prioritizes SERP results depending on the location of users, showing information such as comments from other users, distance, price, addresses, and contacts among other information.
Where does this information come from? From Google My Business!
Since it’s a Google product, users need to have a mandatory Google account (it can be registered with a company email address, Gmail or any other domain).
Once the email is sent, users need to create a company page on Google +, confirm the information with Google and access comment data, peak times, contacts, recommendations, photographs, etc., for local searches that have to do with a business or name of a company.
However, we must keep something in mind: even if these steps are taken doesn’t mean the company is going to appear on the SERP when someone who is close conducts a search.
This depends on some factors such as:
- Competition
- Richness of the information
- Authority
Then, the more you plan the submitted data, the greater the likelihood of having displayed data on the SERP.
2.- Take advantage of the richness in a Twitter search to understand what users are talking about
Everyone knows that Twitter is a good social network to distribute content, follow trends, interact, etc. But, did you know that Twitter is also the owner of a powerful search engine/investigation tool?
In addition to searches conducted by users and hashtags, you can find practically anything on this Social Network if you use the right command.
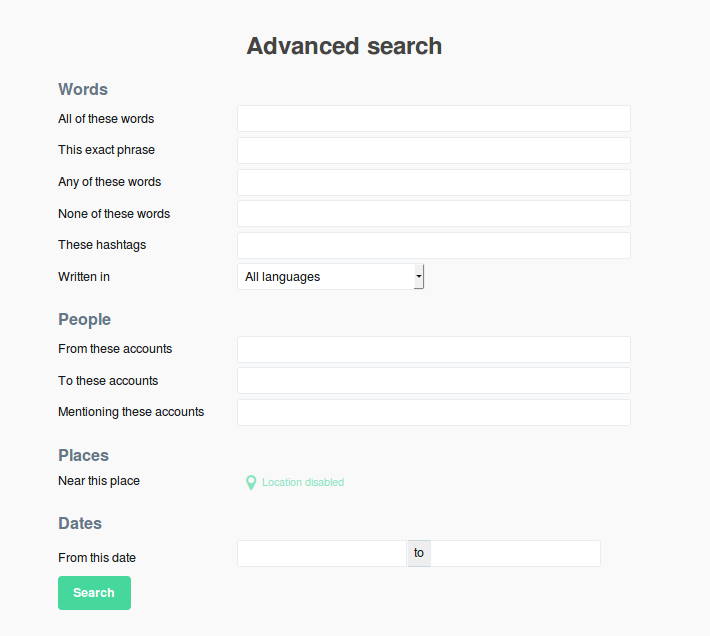
As usual, valuable information is hidden. When you conduct a search, Twitter is not clear about its search power.
But all you need to do is access the search filter “advanced search” to find out how the magic happens.
This is a robust search engine with optimal use and several filter options. From there the sky is the limit. All you need is an objective in mind and use the search to generate data regarding such objective.
3.- Use social media to understand users’ needs. Talk with them.
In the same way that social networks are useful to distribute content, they are also useful to understand an audience and adapt digital marketing strategies accordingly.
Looking more specifically at Facebook, there are several ways to understand the behavior of an audience and adapt your SEO strategy.
Facebook has 2 ways to analyze an audience:
- Audience Insights
- Graph Search
To access Audience Insights, all you need to do is be an administrator of a page. You can analyze Facebook as a whole or as a specific page (for a wealth of data you must have more than 1,000 likes).
It’s possible to analyze interests, gender, if the user uses a desktop or a mobile phone more, pages that have more connection with an audience, among other data.
In the case of Graphsearch, I can say it has its own power, since, in a certain way, Facebook turns into in a huge database.
To access Graphsearch, you don’t need to be an administrator of a page, but the Facebook language must be set up in English.
This way, the search field on Facebook is turned into a tool similar to a giant database bank of this Social Network.
There are thousands of available options, such as how to discover why groups of people follow a certain page, what groups a certain person participates with, photographs or videos of people who were in a specific country or event, among many other search options.
Since there are thousands of commands, let me share the post of Jon Loomer, even though he is old, he continues to be useful, with several Graph Search commands.
Using social media to position a site is not something Google likes. If you stop to think about it, you realize that social media offer areas to interact with possible clients or customers. If you use them as branding vehicles and relationship builders, you obtain powerful data that can help you plan content strategies for a blog, product, brand, and impact SEO directly.
Contrary to what many people think, the exact reasoning behind “ranking for x term” isn’t the right path. SERPs are more intelligent and customized so it’s really important to understand who your users are and what they need.
This way you can create the right content for them, keeping Google happy since it values the users’ experience.
Here at Search Lab, we work on SEO in a humane way putting emphasis on positioning elements according to the needs of our users.
We hope this was useful! Please share this post so it can help others as well.
_____________
About the Author
 Victor Baptista, Advertising expert with more than 10 years of experience in digital projects of various industries. In addition, he teaches in several educational institutions in Rio de Janeiro and is the founder of Marketagem y co-founder of Search Lab.
Victor Baptista, Advertising expert with more than 10 years of experience in digital projects of various industries. In addition, he teaches in several educational institutions in Rio de Janeiro and is the founder of Marketagem y co-founder of Search Lab.
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/victor-baptista/.